Difference between revisions of "Tesla Bosch Radar"
m (→Modifying the configuration file for radar) |
m (→Obtain the VIN programmed in your radar) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
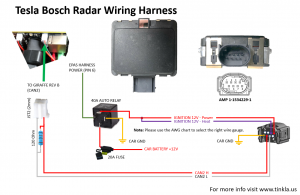
For a permanent install I recommend following the diagram in the Tesla Bosch Radar Wiring Harness image at the top of the page. This setup uses the EPAS power (which is ignition power) to trigger a relay and feed power to both the radar electronics and the heater unit of the radar. Make sure the line from the battery is fused. Also please use the [[AWG chart]] to select the right wire needed for your setup. | For a permanent install I recommend following the diagram in the Tesla Bosch Radar Wiring Harness image at the top of the page. This setup uses the EPAS power (which is ignition power) to trigger a relay and feed power to both the radar electronics and the heater unit of the radar. Make sure the line from the battery is fused. Also please use the [[AWG chart]] to select the right wire needed for your setup. | ||
| − | === | + | === Modifying the configuration settings for radar === |
| + | |||
| + | Now that we have the VIN, we need to configure the [[OpenPilot Configuration File]] with the needed parameters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [OP_CONFIG] | ||
| + | use_tesla_radar = True | ||
| + | enable_radar_emulation = True | ||
| + | radar_vin = YOUR_RADAR_VIN_HERE | ||
| + | radar_offset = 0.0 | ||
| + | radar_epas_type = 0 | ||
| + | radar_position = 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | So make sure that the '''use_tesla_radar''' variable is set to True. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''radar_vin''' need to match the VIN you obtain from the readRadarVin.py script (do not put any quotes or any other characters on that line, just the VIN). Example: '''5YJSA1E41FF156789''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''radar_offset''' has to be changed only if your radar is not centered on the car (some cars have it closer to the left side of the car, in which case the offset should be positive and equal to the distance between the center of the radar and center of the car, in meters; for example 58cm will be 0.58 for offset). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following settings need to match the values that were on '''the donor car''', not your car. Use the [https://teslatap.com/vin-decoder/ VIN Decoder] to understand the Tesla model, year and other information that can help you program these parameters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''radar_epas_type''' is the type of EPAS that was on the donor car. The value can be between 0 and 4: | ||
| + | * 0 - Bosch L538 | ||
| + | * 1 - Bosch L405 | ||
| + | * 2 - Mando FGR64 | ||
| + | * 3 - Mando VGR66 | ||
| + | * 4 - Mando VGR66 Gen3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | For pre-facelift AP1 cars you will find mostly 0 or 1. Post facelift cars are mostly 3 or 4. But nothing can give you the exact value and you might have to try various values until RADC_a062_strRackMismatch in TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message is 0. See the [[Tesla_Bosch_Radar#Troubleshooting_the_Tesla_Bosch_Radar|troubleshooting section]] to learn how to look at the TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message in [[Cabana]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''radar_position''' is the position of the radar in the donor car. The value can be between 0 and 2: | ||
| + | * 0 - Model S (pre facelift) | ||
| + | * 1 - Model S (post facelift) | ||
| + | * 2 - Model X | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can use the manufacturing date and model from [https://teslatap.com/vin-decoder/ VIN Decoder] to estimate your value. 2014 and 2015 Model S will always be 0. 2017 and above Model S will be 1. Model X will be always 2. But again nothing will give you the exact value and you might have to try 0 or 1 if the Model S was manufactured in 2016 because it could be 0 (pre April 2016) or 1 (post April 2016). The value of RADC_a061_radPositionMismatch in TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message should be 0 if programmed correctly. See the [[Tesla_Bosch_Radar#Troubleshooting_the_Tesla_Bosch_Radar|troubleshooting section]] to learn how to look at the TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message in [[Cabana]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can find an explanation of each of the parameters [[OpenPilot Configuration File|here]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once done, reboot your EON. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Programming your radar - VIN Learning === | ||
Chances are you bought your Tesla Bosch Radar on ebay and was previously installed and programmed in a car (so it will only respond if we send the right VIN, epay type and position). The first step in getting the radar to send data is to obtain the VIN that was previously programmed. To get the VIN you will have to use the [https://github.com/BogGyver/openpilot/blob/test_teslaradar/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/readRadarVin.py readRadarVin.py] script (if you are on one of my branches the file is located in <source inline>/data/openpilot/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/</source>). | Chances are you bought your Tesla Bosch Radar on ebay and was previously installed and programmed in a car (so it will only respond if we send the right VIN, epay type and position). The first step in getting the radar to send data is to obtain the VIN that was previously programmed. To get the VIN you will have to use the [https://github.com/BogGyver/openpilot/blob/test_teslaradar/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/readRadarVin.py readRadarVin.py] script (if you are on one of my branches the file is located in <source inline>/data/openpilot/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/</source>). | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 26 March 2022
If you need instructions for the Tesla Bosch Radar to use with EON or other (non Tesla) cars, the information can be found here.
The Bosch radar made for Tesla (Bosch MRRevo14, and with few different part numbers like 1038224-00-A/B or 1057551-00-B) have been used on Tesla Model S cars from October 2014 (AP1) until they have been replaced by the Continental radar with AP2.5). The main difference between 1038224-00-B and 1038224-00-A is that the A version does not have the heater element for winter weather (to melt snow and ice).
The radar has a range of about 160m and for the short beam a cone of 45°.
Contents
Bosch radars
Many other car manufacturers use the same radar hardware, including Honda, Nissan, VW, Audi, etc. But Tesla (AFAIK) is the only one that reads and processes raw data from the radar instead of letting the radar make the decision about longitudinal control action needed (acceleration or deceleration).
This radar can ben used on any OP supported car. To insall the radar for a non-Tesla car please find a branch that has the code already done or modify your branch and add the code needed to make the radar talk to the Panda code for your car. More info available here.
Deconding the radar
With a little help from a group of enthusiasts, we were able to reverse engineer all the messages that AP sends to the radar in order to make it "talk". Then we identified the structure of the CAN messages that describe each of the 32 objects this radar can detect. Signals like longitudinal distance, lateral distance (vs radar), longitudinal relative speed, lateral relative speed, longitudinal acceleration, certainty of detection, etc are all now processed and sent to the radar daemon of OpenPilot, improving longitudinal control for the car.
What you need
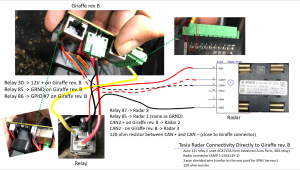
In order to get the radar working on your car, you need to buy a radar, a mounting bracket (few options here), a connector and then to create a harness and run the cable back to the Tinkla OBD-C Adapter.
For a permanent install I recommend following the diagram in the Tesla Bosch Radar Wiring Harness image at the top of the page. This setup uses the EPAS power (which is ignition power) to trigger a relay and feed power to both the radar electronics and the heater unit of the radar. Make sure the line from the battery is fused. Also please use the AWG chart to select the right wire needed for your setup.
Modifying the configuration settings for radar
Now that we have the VIN, we need to configure the OpenPilot Configuration File with the needed parameters.
[OP_CONFIG] use_tesla_radar = True enable_radar_emulation = True radar_vin = YOUR_RADAR_VIN_HERE radar_offset = 0.0 radar_epas_type = 0 radar_position = 0
So make sure that the use_tesla_radar variable is set to True.
radar_vin need to match the VIN you obtain from the readRadarVin.py script (do not put any quotes or any other characters on that line, just the VIN). Example: 5YJSA1E41FF156789
radar_offset has to be changed only if your radar is not centered on the car (some cars have it closer to the left side of the car, in which case the offset should be positive and equal to the distance between the center of the radar and center of the car, in meters; for example 58cm will be 0.58 for offset).
The following settings need to match the values that were on the donor car, not your car. Use the VIN Decoder to understand the Tesla model, year and other information that can help you program these parameters.
radar_epas_type is the type of EPAS that was on the donor car. The value can be between 0 and 4:
- 0 - Bosch L538
- 1 - Bosch L405
- 2 - Mando FGR64
- 3 - Mando VGR66
- 4 - Mando VGR66 Gen3
For pre-facelift AP1 cars you will find mostly 0 or 1. Post facelift cars are mostly 3 or 4. But nothing can give you the exact value and you might have to try various values until RADC_a062_strRackMismatch in TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message is 0. See the troubleshooting section to learn how to look at the TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message in Cabana.
radar_position is the position of the radar in the donor car. The value can be between 0 and 2:
- 0 - Model S (pre facelift)
- 1 - Model S (post facelift)
- 2 - Model X
You can use the manufacturing date and model from VIN Decoder to estimate your value. 2014 and 2015 Model S will always be 0. 2017 and above Model S will be 1. Model X will be always 2. But again nothing will give you the exact value and you might have to try 0 or 1 if the Model S was manufactured in 2016 because it could be 0 (pre April 2016) or 1 (post April 2016). The value of RADC_a061_radPositionMismatch in TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message should be 0 if programmed correctly. See the troubleshooting section to learn how to look at the TeslaRadarAlertMatrix message in Cabana.
You can find an explanation of each of the parameters here.
Once done, reboot your EON.
Programming your radar - VIN Learning
Chances are you bought your Tesla Bosch Radar on ebay and was previously installed and programmed in a car (so it will only respond if we send the right VIN, epay type and position). The first step in getting the radar to send data is to obtain the VIN that was previously programmed. To get the VIN you will have to use the readRadarVin.py script (if you are on one of my branches the file is located in /data/openpilot/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/).
Once you have the scrip do the following steps:
- SSH into the EON
cd /data/openpilot/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/(or go to the location where you saved the script)- kill OpenPilot:
tmux kill-session -t comma
- set the python environment variable
export PYTHONPATH="/data/openpilot/"
- run the readRadarVin.py script
python readRadarVin.py
The 17 character VIN number will be displayed in the output of the script. Write it down. It should look something like 5YJSA1E41FF156789
Calibrating your radar
Most likely the radar will have to be calibrated in order to ensure the correct data being fed into OpenPilot. In order to calibrate your radar you will need:
- the calibrateRadar.py script which for those running on one of my Tesla branches is located in /data/openpilot/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/
- a 4ft (120 cm) metal pole that can stay vertically by itself (I personally use a microphone stand)
- tape measure
- chalk
- computer or phone to SSH into EON and view data
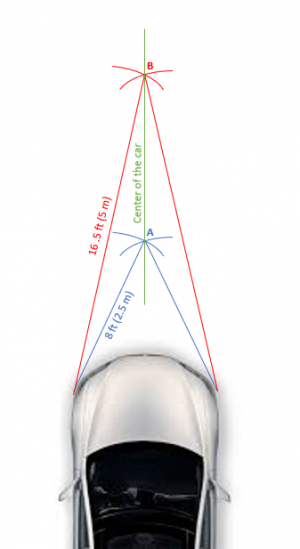
First, we need to create a straight line that is perfectly centered on the car (for this you will need another person to hold one end of the tape). Follow these steps:
- start from the left front wheel well, measure 8 ft (2.5m) out towards the center of the car and draw an arch of the circle using the chalk.
- repeat the process from the right front wheel
- the place where your two arches intersect will be point A. (see blue lines in diagram)
- repeat the process above but measure out 16.5 ft (5 m)
- the place where your two new arches intersect will be point B (see red lines in diagram)
- connect points A and B with a line; this line is now along the center of the car (see green line in diagram)
Now that we have the line that marks the zero dY line, let's start the calibration script:
- start OP (OP might stop when you leave the car; what i did was to put open the driver window, put a heavy backpack on the driver seat, connect the driver seatbelt and turn the car on; this way it ensured that OP remained running)
- SSH into EON and go to the folder where the calibrateRadar.py is
cd /data/openpilot/selfdrive/car/tesla/radar_tools/
- set the python environment
export PYTHONPATH="/data/openpilot/"
- run the calibration script
python calibrateRadar.py
The script will start showing data for objects between 8 ft (2.5 m) and 15 ft (4.5 m) in front of the car.
Now the calibration process starts:
- place the metal pole (again, i used a microphne stand) in the middle of the line that connects A and B
- look at the terminal window running the calibration script and check x and y values for distance:
- you should see data from the script showing dRel and dY as some of the points; keep in mind the values are always in meters
- measure the distance between the radar and the pole: it should match the dRel distance
- dY should be 0.0
- if you can not see the pole at all or dRel is greater than the real measured distance, you will need to adjust the radar vertically until they match.
- if dY is not zero, adjust the radar position Left or Right until dY is 0.0
- once dY is 0.0 move the pole along the line connecting A and B repeating the above process
- you are done when no matter where you place the pole between A and B, dY is always 0.0
Troubleshooting the Tesla Bosch Radar
The radar send data for the first 5 seconds no matter what we send to it. But if we are sending the wrong info (VIN, position or epas) it will stop sending changes to the data after 5 seconds. At this point we have to see what exactly is happening with the radar by looking at the allerts it generates.
You can use cabana and paste the following code in the DBC in order to understand what errors the radar is sending and what you need to change. Once you opened your cabana drive, click Load DBC, then Upload, and copy and paste the content from below to the DBC area. Then just look at the message called TeslaRadarAlertMatrix and see if you have any errors. Calibration warnings will not stop radar from operating. (Make sure you're looking at 1:501 for TeslaRadarAlertMatrix, not 0:501)
VERSION "" NS_ : NS_DESC_ CM_ BA_DEF_ BA_ VAL_ CAT_DEF_ CAT_ FILTER BA_DEF_DEF_ EV_DATA_ ENVVAR_DATA_ SGTYPE_ SGTYPE_VAL_ BA_DEF_SGTYPE_ BA_SGTYPE_ SIG_TYPE_REF_ VAL_TABLE_ SIG_GROUP_ SIG_VALTYPE_ SIGTYPE_VALTYPE_ BO_TX_BU_ BA_DEF_REL_ BA_REL_ BA_DEF_DEF_REL_ BU_SG_REL_ BU_EV_REL_ BU_BO_REL_ SG_MUL_VAL_ BS_: BU_: FrontCamera Radar BO_ 769 TeslaRadarSguInfo: 8 Radar SG_ RADC_VerticalMisalignment : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|255] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_SCUTemperature : 8|8@1+ (1,-128) [-128|127] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_VMA_Plaus : 16|8@1+ (1,0) [0|255] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_SGU_ITC : 24|8@1+ (1,0) [0|255] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_HorizontMisalignment : 32|12@1+ (1,0) [0|4096] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_SensorDirty : 44|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_HWFail : 45|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_SGUFail : 46|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_SGUInfoConsistBit : 47|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera BO_ 770 TeslaRadarTguInfo: 8 Radar SG_ RADC_ACCTargObj1_sguIndex : 0|6@1+ (1,0) [0|63] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_ACCTargObj2_sguIndex : 6|6@1+ (1,0) [0|63] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_ACCTargObj3_sguIndex : 12|6@1+ (1,0) [0|63] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_ACCTargObj4_sguIndex : 18|6@1+ (1,0) [0|63] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_ACCTargObj5_sguIndex : 24|6@1+ (1,0) [0|63] "" FrontCamera SG_ unused30 : 30|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_TGUInfoConsistBit : 31|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_ACCTargObj1_dBPower : 32|16@1+ (1,0) [0|65535] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_ACCTargObj5_dBPower : 48|16@1+ (1,0) [0|65535] "" FrontCamera BO_ 1281 TeslaRadarAlertMatrix: 8 Radar SG_ RADC_a001_ecuInternalPerf : 0|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a002_flashPerformance : 1|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a003_vBatHigh : 2|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a004_adjustmentNotDone : 3|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a005_adjustmentReq : 4|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a006_adjustmentNotOk : 5|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a007_sensorBlinded : 6|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a008_plantModeActive : 7|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a009_configMismatch : 8|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a010_canBusOff : 9|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a011_bdyMIA : 10|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a012_espMIA : 11|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a013_gtwMIA : 12|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a014_sccmMIA : 13|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a015_adasMIA : 14|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a016_bdyInvalidCount : 15|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a017_adasInvalidCount : 16|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a018_espInvalidCount : 17|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a019_sccmInvalidCount : 18|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a020_bdyInvalidChkSm : 19|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a021_espInvalidChkSm : 20|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a022_sccmInvalidChkSm : 21|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a023_sccmInvalidChkSm : 22|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a024_absValidity : 23|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a025_ambTValidity : 24|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a026_brakeValidity : 25|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a027_CntryCdValidity : 26|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a028_espValidity : 27|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a029_longAccOffValidity : 28|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a030_longAccValidity : 29|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a031_odoValidity : 30|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a032_gearValidity : 31|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a033_steerAngValidity : 32|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a034_steerAngSpdValidity : 33|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a035_indctrValidity : 34|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a036_vehStandStillValidity : 35|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a037_vinValidity : 36|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a038_whlRotValidity : 37|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a039_whlSpdValidity : 38|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a040_whlStandStillValidity : 39|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a041_wiperValidity : 40|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a042_xwdValidity : 41|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a043_yawOffValidity : 42|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a044_yawValidity : 43|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a045_bsdSanity : 44|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a046_rctaSanity : 45|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a047_lcwSanity : 46|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a048_steerAngOffSanity : 47|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a049_tireSizeSanity : 48|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a050_velocitySanity : 49|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a051_yawSanity : 50|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a052_radomeHtrInop : 51|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a053_espmodValidity : 52|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a054_gtwmodValidity : 53|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a055_stwmodValidity : 54|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a056_bcmodValidity : 55|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a057_dimodValidity : 56|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a058_opmodValidity : 57|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a059_drmiInvalidChkSm : 58|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a060_drmiInvalidCount : 59|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a061_radPositionMismatch : 60|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ RADC_a062_strRackMismatch : 61|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" FrontCamera SG_ unused62 : 62|2@1+ (1,0) [0|3] "" FrontCamera